What ISO 27001 Is and Why It Matters
ISO 27001 is the international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), that guides organizations to identify information assets, assess risks systematically, implement appropriate controls, and demonstrate continuous improvement. It takes a holistic approach to managing sensitive information across people, processes, and technology to create a sustainable security program that evolves along with business needs and emerging threats.
Global Relevance and Industries Adopting It
ISO 27001 certification is valuable for organizations of all sizes. This widespread acceptance stems from its technology-agnostic approach and alignment with diverse regulatory requirements worldwide.
Technology sector: Software companies, cloud providers, and fintech firms use ISO 27001 to demonstrate security maturity to enterprise customers.
Financial services: Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies leverage ISO 27001 to meet regulatory expectations while protecting sensitive data.
Healthcare: Healthcare providers and health technology companies implement ISO 27001 to safeguard patient information while supporting compliance efforts.
Government and defense: Public sector organizations adopt ISO 27001 to protect citizen data and sensitive government information, often as part of broader cybersecurity initiatives.
Manufacturing and supply chain: Industrial companies use ISO 27001 to protect intellectual property and secure increasingly connected manufacturing systems against cyber threats.
Benefits of ISO 27001 Certification
Enhanced customer trust: It serves as a powerful trust signal as it demonstrates a commitment to protecting information and sensitive data.
Systematic risk reduction: Beyond compliance, ISO 27001 implementation typically reduces security incidents by helping to identify vulnerabilities before they become breaches.
Operational efficiency: Organizations often discover that ISO 27001 implementation streamlines security processes, eliminates redundant controls, and provides clearer accountability structures.
Competitive advantage: In markets where security is a differentiator, ISO 27001 certification can command premium pricing, preferred vendor status, and expansions into new markets.
Core Components of ISO 27001
Information Security Management System (ISMS)
The ISMS is ISO 27001's core framework, integrating security policies, procedures, and controls into your organization's management structure. It provides systematic governance that aligns security with business objectives and ensures consistent protection across all assets.
Key components include:
A three-tier policy framework (policies, procedures, work instructions)
Security integrated into daily business processes
Clear governance with defined roles and oversight
KPIs that measure effectiveness through metrics like incident detection speed, patching rates, and training completion
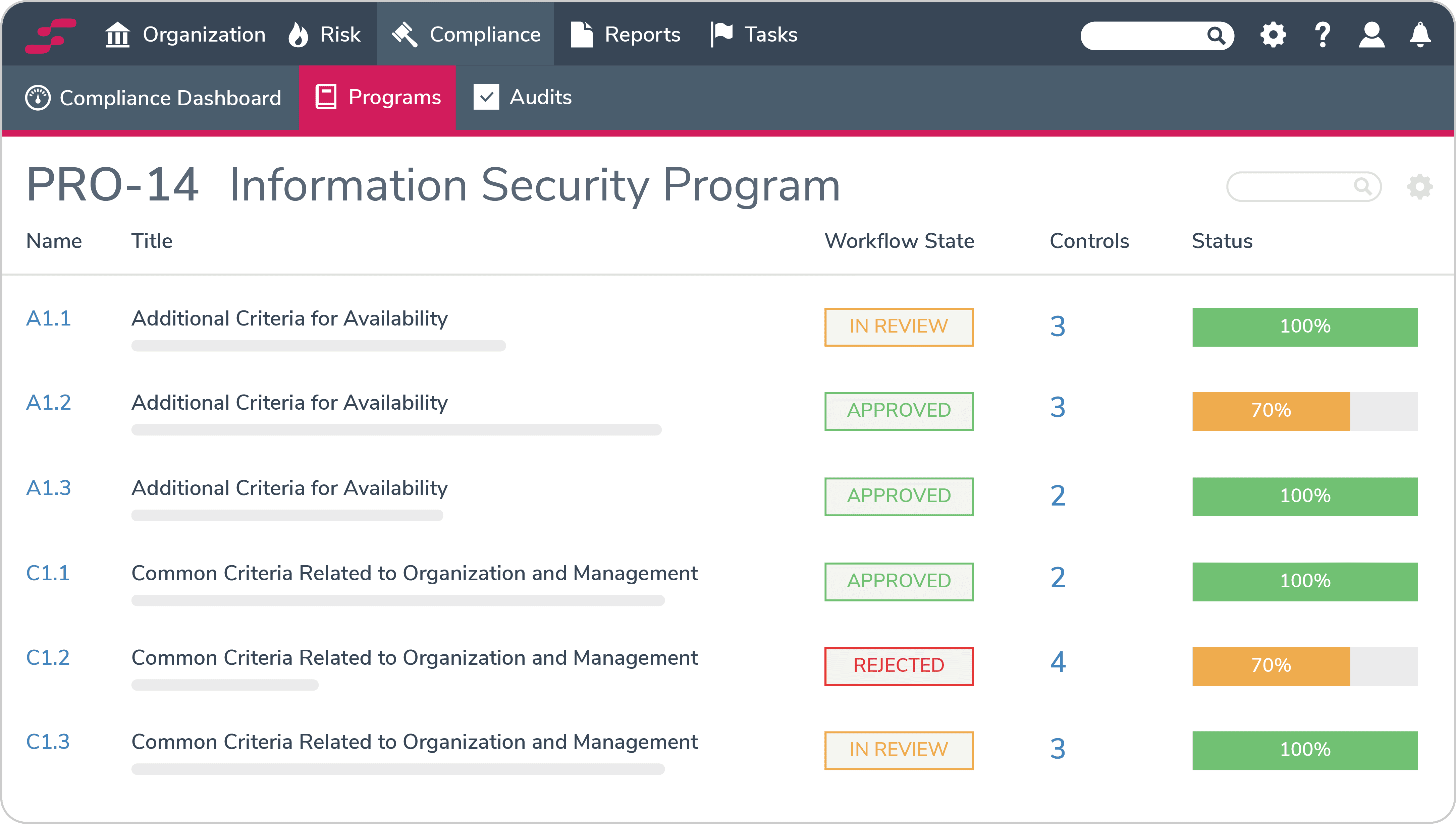
Annex A Controls Overview
Annex A provides 93 specific security controls organized into four areas; these represent best practices distilled from decades of information security experience across diverse industries and threat environments.
Organizational controls (14 categories)
People controls (8 categories)
Physical and environmental controls (14 categories)
Technological controls (34 categories)
Organizations don't need to implement every Annex A control. The risk assessment process determines which controls are applicable based on identified risks, business requirements, and legal obligations to focus resources on controls that provide the greatest security value.
How Does Risk Management Factor into ISO 27001 Compliance?
Risk management forms the cornerstone of ISO 27001, requiring organizations to:
Evaluate risks
Treat risks
Monitor risks
This process moves beyond reactive security measures to create data-driven security programs aligned with business objectives.
The ISO 27001 Certification Process
Following the steps towards ISO 27001 certification ensures your organization’s ISMS practices align with global best practices, and regulatory requirements to foster trust, resilience, and integrity in the organization’s operations.
Gap Assessment
Compare current security policies and controls against ISO 27001 requirements to identify gaps and prioritize improvements. Define your ISMS scope, form a cross-functional team, secure leadership support, and ensure understanding of Clauses 4-10 and Annex A controls.
ISMS Implementation
Build an operational ISMS by establishing a risk management framework, developing policies and procedures, and deploying controls. Review Annex A controls, create a Statement of Applicability (SOA), integrate security into business processes, and provide cybersecurity training to embed the ISMS into daily workflows.
Internal Audit
Validate ISMS effectiveness through internal audits before certification. Organize all documentation, schedule audits, document findings, and implement corrective actions. Select an accredited certification body and schedule Stage 1 (documentation review) and Stage 2 (implementation assessment) audits.
Certification Audit (Stage 1 & 2)
Stage 1 reviews documentation and readiness; Stage 2 tests implementation through interviews and evidence review. Resolve all major issues and address minor findings. Upon successful completion, certification is valid for three years.
Ongoing Surveillance Audits
Annual surveillance audits monitor selected ISMS areas and performance. Maintain certification through continuous improvement, regular risk assessment updates, and addressing emerging threats. Recertification is required every three years.
Common ISO 27001 Challenges
Documentation Overload and Policy Upkeep
Many organizations get buried under excessive documentation when trying to meet ISO 27001 requirements. Creating too many separate policies and procedures leads to inconsistencies, outdated documents, and confusion for users.
Manual Evidence Collection and Audit Prep
Gathering audit evidence manually is time-consuming and error prone. Evidence often lives across multiple systems (IT, HR, facilities), making it hard to track and leaving gaps during audits. Teams typically scramble right before an audit, increasing stress and the chance of missing critical evidence.
Third-Party Risk Visibility
Vendors and partners expand the attack surface, but many organizations struggle to assess and monitor them effectively. Questionnaires offer only snapshots, while ongoing monitoring is often missing. Security issues may only surface during incidents or annual reviews. Incident coordination and weak vendor contracts further complicate compliance, leaving organizations exposed.
Keeping Pace with Regulatory Change
Organizations rarely deal with ISO 27001 alone, GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others often overlap. Regulations change quickly, are sometimes ambiguous, and require significant resources to interpret and implement. Balancing new requirements with existing compliance and day-to-day security needs stretches limited budgets and teams.
Sustaining Compliance After Certification
Getting certified is often easier than staying compliant in the long-term. After the initial push, organizations risk becoming complacent, cutting budgets, or losing key personnel. Outdated processes, evolving technology, and weak governance structures make it easy to slip out of compliance.
How GRC Software Simplifies ISO 27001
Modern GRC platforms replace manual, document-heavy processes with dynamic systems that improve compliance and efficiency.
Automated Risk Register: Transforms spreadsheets into integrated systems that identify, analyze, and track risks in real time with dynamic integrations, quantitative analysis, centralized treatment tracking, and customizable dashboards for executive and operational visibility.
Continuous Evidence Collection: Automatically captures compliance evidence from systems, eliminating manual audit prep. Conducts ongoing testing to validate control effectiveness, maintains audit-ready packages in centralized repositories, and provides real-time monitoring that flags missing evidence or control failures.
Audit Readiness: Simplifies audits through automated audit trails, self-service auditor access, and gap analysis reporting. Centralized audit project management reduces business disruption while ensuring transparency and effective remediation tracking.
Framework Mapping: Aligns ISO 27001 with multiple frameworks through integrated control mapping, reducing duplicate work via unified evidence collection and harmonized reporting while optimizing resource allocation across overlapping requirements.
Best Practices for Achieving and Maintaining ISO 27001
Executive Buy-in & Clear Ownership
Executive engagement is critical for success. Leaders must champion security as a business enabler, commit resources for implementation and ongoing operations, and actively participate in governance through management reviews and risk decisions. Designate executive sponsors with clear reporting relationships and success metrics to ensure accountability.
Early Gap Assessment & Remediation Roadmap
Conduct a comprehensive baseline assessment of current security across governance, risk management, technical controls, and personnel practices. Prioritize remediation by risk level and complexity, establish realistic resource plans with contingencies, and set clear milestones while integrating change management to minimize disruption.
Build a Culture of Security Awareness
Transform compliance into organizational values through leadership modeling and visible commitment. Deliver role-specific training using interactive, scenario-based content with regular reinforcement. Align recognition and incentives with security behaviors and establish feedback mechanisms for open communication without blame.
Leverage Automation for Evidence & Monitoring
Integrate GRC platforms to automatically collect compliance evidence and reduce manual effort. Implement continuous monitoring with automated testing, configuration management, and prioritized alerting systems. Generate automated reports for compliance tracking and management briefings while maintaining backup procedures.
Continuous Improvement Mindset
Establish KPIs measuring incident response times, risk management outcomes, and control effectiveness. Systematically capture lessons from incidents, audits, and operations to drive improvements. Benchmark against industry peers and integrate security planning with business strategy to ensure alignment with evolving objectives and threats.