
All-In-One GRC Software


Manage all your GRC activities from one central platform, boosting efficiency and reinforcing trust across every level of your organization.









Build trust and drive growth
StandardFusion GRC Software
StandardFusion GRC Software



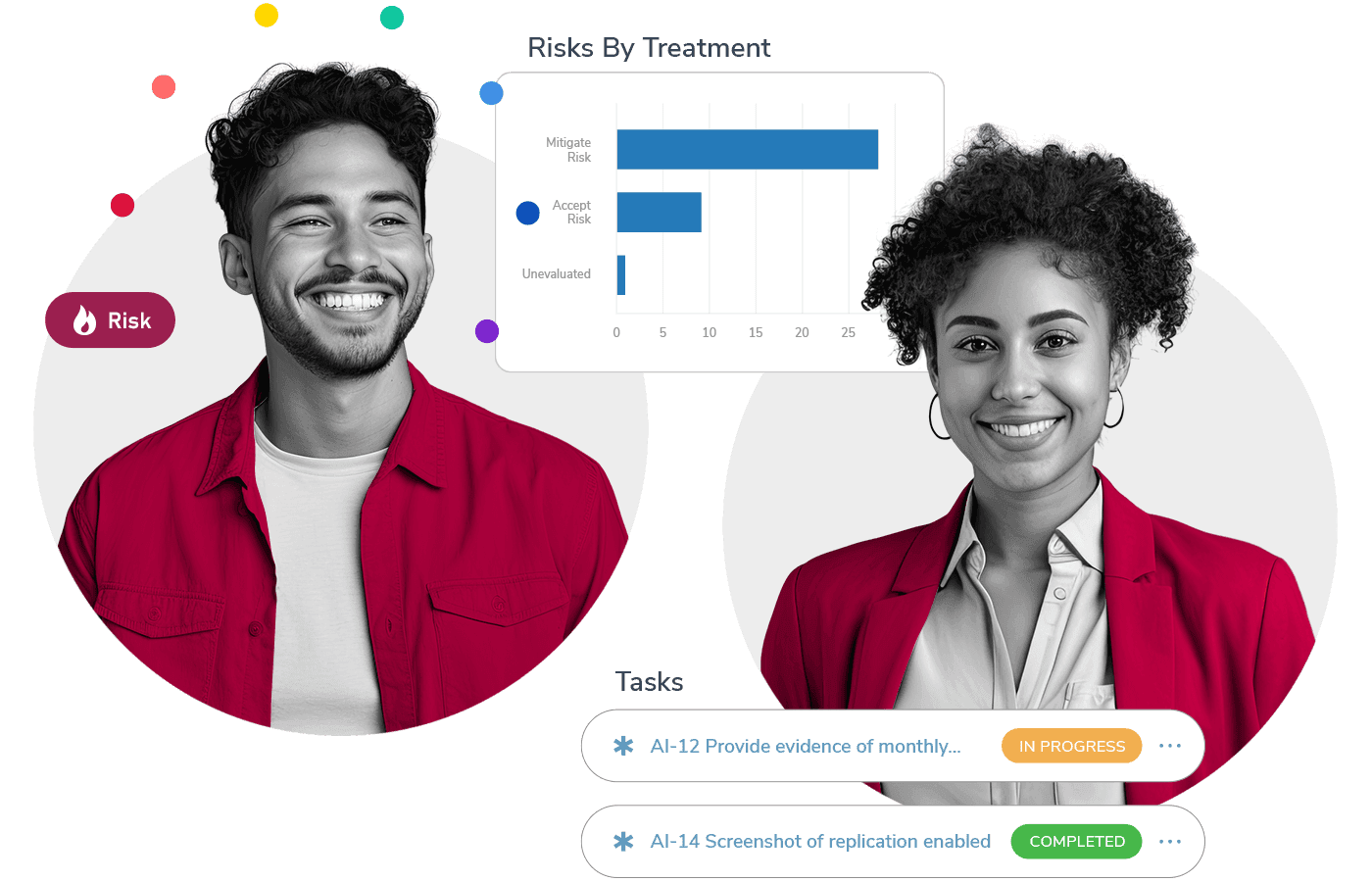
Risk Management
Foster a proactive, risk-aware culture that turns potential threats into strategic opportunities for growth.




StandardFusion GRC
Centralized and adaptive GRC platform that gives you clarity and consistency, building trust and integrity across your organization.



Compliance Management
Ensure enterprise-wide adherence, simplifying compliance processes for transparency and growth.
Everything in One Place
Manage all your GRC needs in one place. This centralized approach boosts efficiency, fosters trust, and reduces complexity, helping your team focus on what matters.

Flexible to Your Needs
Tailor your platform to integrate smoothly with your unique needs and enhance your workflows without disrupting the daily rhythm of your team and operations.
Grow Your Way
As your organization expands, so does your capability to manage risks and compliance. Stay ahead of the curve with a GRC tool that scales with your growth.

Everything in One Place
Manage all your GRC needs in one place. This centralized approach boosts efficiency, fosters trust, and reduces complexity, helping your team focus on what matters.


Flexible to Your Needs
Tailor your platform to integrate smoothly with your unique needs and enhance your workflows without disrupting the daily rhythm of your team and operations.
Grow Your Way
As your organization expands, so does your capability to manage risks and compliance. Stay ahead of the curve with a GRC tool that scales with your growth.

Everything in One Place
Manage all your GRC needs in one place. This centralized approach boosts efficiency, fosters trust, and reduces complexity, helping your team focus on what matters.
Flexible to Your Needs
Tailor your platform to integrate smoothly with your unique needs and enhance your workflows without disrupting the daily rhythm of your team and operations.
Grow Your Way
As your organization expands, so does your capability to manage risks and compliance. Stay ahead of the curve with a GRC tool that scales with your growth.


From Spreadsheets to an All-in-One GRC Platform
Discover how StandardFusion’s journey led to a scalable, all-in-one GRC platform that fosters trust and integrity.


From Spreadsheets to an All-in-One GRC Platform
Discover how StandardFusion’s journey led to a scalable, all-in-one GRC platform that fosters trust and integrity.


From Spreadsheets to an All-in-One GRC Platform
Discover how StandardFusion’s journey led to a scalable, all-in-one GRC platform that fosters trust and integrity.



Optimize Your Workflow With Powerful Integrations
Extend your GRC capabilities seamlessly, integrating tools for cohesive and transparent workflows across your organization.

Advanced Enterprise-Grade Configuration Options
Conquer GRC complexities with a solution designed for your unique needs, promoting efficient workflows and cohesive management


Advanced Enterprise-Grade Configuration Options
Conquer GRC complexities with a solution designed for your unique needs, promoting efficient workflows and cohesive management


Advanced Enterprise-Grade Configuration Options
Conquer GRC complexities with a solution designed for your unique needs, promoting efficient workflows and cohesive management

Embrace A Proactive Approach To GRC

“We can demonstrate how we are enabling clients to meet their compliance objectives.”
Sandy B.
CSO


“We are able to maximize our time spent on audit and compliance allocating time effectively.”
Michael G.
COO


“StandardFusion is really easy to use and provides all the best features under one roof.”
Rajbhushan S.
bd manager


“Its intuitive user interface provides a wealth of valuable, helpful information.”
Prince S.
Risk & Compliance Lead

Embrace A Proactive Approach To GRC

“We can demonstrate how we are enabling clients to meet their compliance objectives.”
Sandy B.
CSO


“We are able to maximize our time spent on audit and compliance allocating time effectively.”
Michael G.
COO


“StandardFusion is really easy to use and provides all the best features under one roof.”
Rajbhushan S.
bd manager


“Its intuitive user interface provides a wealth of valuable, helpful information.”
Prince S.
Risk & Compliance Lead

Embrace A Proactive Approach To GRC

“We can demonstrate how we are enabling clients to meet their compliance objectives.”
Sandy B.
CSO


“We are able to maximize our time spent on audit and compliance allocating time effectively.”
Michael G.
COO


“StandardFusion is really easy to use and provides all the best features under one roof.”
Rajbhushan S.
bd manager


“Its intuitive user interface provides a wealth of valuable, helpful information.”
Prince S.
Risk & Compliance Lead

Solutions
Company
Copyright © 2015 - 2025 StandardFusion. All Rights Reserved.
Solutions
Company
Copyright © 2015 - 2025 StandardFusion. All Rights Reserved.
Solutions
Company
Copyright © 2015 - 2025 StandardFusion. All Rights Reserved.
