Published on: Mar 20, 2024
ISO 27000 Series of Standards: Everything You Need to Know
If you are a business owner or an IT professional, you might have heard of the ISO/IEC 27000 series of standards. These are international standards that provide guidance and best practices for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an information security management system (ISMS).
An ISMS is a systematic approach to managing the security of your information assets. This includes data, systems, networks, devices, and people.
But what exactly is the ISO/IEC 27000 series and how can it help you achieve your information security goals?
In this article, we will answer these questions and more.
We will explain the basics of the ISO/IEC 27000 series, its benefits and challenges, and how you can apply it to your organization simply and effectively.
Let's begin!
What is the ISO/IEC 27000 Series of Standards?
The ISO/IEC 27000 series is a family of standards that covers various aspects of information security management. The most well-known and widely used standard is ISO/IEC 27001, which specifies the requirements for an ISMS. It also provides a framework for assessing and certifying the compliance of an organization's ISMS with the standard. ISO/IEC 27001 is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which involves:
Planning: defining the scope, objectives, policies, and procedures of the ISMS
Doing: implementing and operating the ISMS according to the policies and procedures
Checking: monitoring and reviewing the performance and effectiveness of the ISMS
Acting: taking corrective and preventive actions to improve the ISMS
ISO/IEC 27001 also refers to other standards in the ISO/IEC 27000 series that provide more detailed guidance on specific topics, such as risk management, controls, auditing, metrics, incident management, business continuity, cloud computing, and more.
These standards are ISO/IEC 27002 to ISO/IEC 27018. You can choose which ones are relevant and applicable to your organization depending on your needs and context.
Comprehensive Overview of ISO 27000 Series
The ISO 27000 series of standards covers various aspects of information security management, such as risk assessment, controls implementation, auditing, certification, and continuous improvement.
The standards are developed and maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The standards are voluntary, but they are widely recognized and adopted by organizations worldwide as a benchmark for information security excellence.
Main Categories of ISO 27000 Series Standards
To make sense of the extensive ISO 27000 family, it helps to break these standards down by their main categories. Each type serves a unique role in building an effective information security management system. Here’s a quick guide to understanding how they are grouped:
Overview and Vocabulary (Informative):
These standards lay the foundation by defining key terms and concepts you’ll encounter throughout the series. They help set the stage and ensure everyone is speaking the same language.Requirements (Normative):
Standards in this category specify exactly what an organization must do to be compliant. These are the rules you need to follow if you want to achieve certification. Only requirements standards, like ISO/IEC 27001, are subject to formal audits.General Guidelines (Informative):
Guideline standards provide practical advice, best practices, and recommended approaches for implementing information security controls, risk management, auditing, and more. They aren’t mandatory, but they help tailor your ISMS to fit organizational needs.Sector-Specific Guidelines (Informative):
These are tailored for specific industries or scenarios—like telecommunications, cloud services, or energy utilities. They address unique challenges and regulatory expectations in different sectors, helping you adapt general principles to your environment.
By understanding these categories, you can better navigate the ISO 27000 series and focus on the standards most relevant to your organization’s goals and compliance needs.
Normative vs. Informative Standards in the ISO/IEC 27000 Series
When exploring the ISO/IEC 27000 series, you'll notice that the standards are divided into two main types: normative and informative. Understanding the difference is helpful when deciding which documents are crucial for compliance—and which are intended to provide guidance or context.
Normative standards set out formal requirements and expectations. They outline what must be done if you wish to claim compliance or seek certification. For example, ISO/IEC 27001 contains specific criteria that your organization's ISMS must meet. Only normative standards are subject to audits, and meeting their requirements is mandatory if you want official certification.
Informative standards, on the other hand, serve as helpful companions. These documents are more descriptive, offering background information, best practice recommendations, and practical advice to help you interpret and implement the normative requirements. They explain concepts, provide context, and often offer examples or guidelines. However, compliance with informative standards is not audited—they’re meant to support your understanding rather than to be enforced.
In short: normative standards set the rules; informative standards help you understand and apply them. Both are important, but only normative ones are necessary for certification.
The ISO 27000 series actually consists of more than 40 standards, each focusing on a specific topic or domain of information security. Some of the most important and relevant standards for businesses and IT professionals are:
ISO/IEC 27000
This overview and vocabulary standard defines the terms and concepts used in the ISO 27000 series. It also provides a high-level framework and principles for implementing and managing an ISMS.
ISO/IEC 27001
This core standard specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an ISMS. It also defines the process for achieving and maintaining certification against the standard. Check this article to learn everything about the latest ISO 27001 version.
An ISMS is a systematic approach to managing the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets in an organization. It involves identifying risks, implementing controls, monitoring performance, and taking corrective actions.
ISO/IEC 27002
This is the code of practice standard that guides how to implement the controls specified in ISO/IEC 27001. It covers 14 domains of information security:
Security policies
Organization of information security
Human resource security
Asset management
Access control
Cryptography
Physical and environmental security
Operations security
Communications security
System acquisition
Development and maintenance
Supplier relationships
Information security incident management
Information security aspects of business continuity management
Compliance
ISO/IEC 27003
This is the implementation guidance standard that provides advice on how to plan and execute an ISMS project based on ISO/IEC 27001. It covers topics such as:
Project initiation
Scoping
Risk assessment
Gap analysis
Implementation plan
Awareness and training
Documentation
Measurement and monitoring
Internal audit
Management review
Certification audit
Continual improvement.
ISO/IEC 27004
This is the measurement standard that guides how to measure and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of an ISMS based on ISO/IEC 27001. It covers topics such as measurement framework, measurement attributes, measurement methods, measurement results analysis and reporting.
ISO/IEC 27005
ISO/IEC 27005 is dedicated to information security risk management, providing organizations with structured guidance on identifying, assessing, and treating risks that could impact their information assets. The standard supports ISO/IEC 27001 by detailing a comprehensive risk management process.
Key recommendations within ISO/IEC 27005 include:
Establishing a risk management framework tailored to the organization's context and objectives.
Systematically identifying threats and vulnerabilities that could affect information security.
Analyzing and evaluating risks to determine their potential impact and likelihood.
Selecting and implementing appropriate risk treatment options—risk avoidance, modification, sharing, or retention.
Continuously monitoring and reviewing risks, controls, and the effectiveness of the risk management program.
Communicating and consulting with stakeholders throughout the risk management process.
This standard ensures that risk management is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing cycle, enabling organizations—regardless of size or sector—to address information security risks proactively and align their practices with international best practices.
ISO/IEC 27006
Provides requirements for bodies that audit and certify organizations against ISO/IEC 27001. It outlines the competence that those performing ISMS audits should possess.
In addition to setting these requirements, ISO/IEC 27006 also guides organizations that offer auditing services and ISMS certification, ensuring they demonstrate competence and reliability in line with ISO 17021. Auditors must be well-versed in the controls, requirements, terminology, principles, references, and legal mandates of ISO/IEC 27001 and 27002. They should also understand how to monitor, measure, evaluate, and analyze ISMS performance, as well as the technicalities of conducting information security audits.
ISO/IEC 27007
Offers detailed guidance on auditing Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). This standard explains how to plan, carry out, and manage ISMS audits—whether internal or external—based on ISO/IEC 27001 requirements. In addition, ISO/IEC 27007 outlines the necessary skills and competencies auditors should have, building on the general auditing principles found in ISO 19011. By following these guidelines, organizations can ensure their ISMS audits are thorough, effective, and aligned with industry best practices.
ISO/IEC TR 27008
Guides evaluating the implementation and operation of information security controls, including those outside the scope of ISO/IEC 27002, offering a broader perspective on ISMS control effectiveness.
By systematically reviewing how controls are applied and maintained, organizations can uncover gaps in their current approach—sometimes referred to as overcoming "paradigm blindness," where established processes may seem sufficient but actually harbor hidden weaknesses. ISO/IEC TR 27008 serves as a practical resource to help organizations identify these gaps, address roadblocks, and ultimately strengthen their security posture and performance. Through regular evaluation using this standard, businesses can not only meet compliance requirements but also discover opportunities for improvement and growth in their information security management.
ISO/IEC 27009
ISO/IEC 27009 serves as a framework for tailoring ISO/IEC 27001 to the unique requirements of various sectors or industries. In essence, this standard guides organizations—and the teams developing sector-specific standards—on how to interpret and adapt the core requirements and controls of ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002 for a particular context.
With ISO/IEC 27009, you can:
Clarify or reinterpret existing ISO/IEC 27001 requirements to suit the nuances of your sector
Add new controls that are especially relevant to your field, even if they're not covered in ISO/IEC 27001 or 27002
Modify or extend existing controls where needed to address sector-specific risks or practices
Update or refine the guidance provided by ISO/IEC 27002 for a more precise application in your organizational environment
This flexibility helps sectors like health care, finance, or critical infrastructure address their distinct regulatory or operational needs—all while staying aligned with the global best practices defined by the ISO/IEC 27000 family.
ISO/IEC 27010
Specifically focused on inter-sector and inter-organizational communications, ISO/IEC 27010 provides guidance tailored to securing information exchanges across different organizations and industries. The standard outlines principles and controls aimed at establishing, implementing, and continually enhancing information security measures when sharing sensitive data externally.
Key topics include:
Establishing trusted channels for data exchange between organizations
Defining roles and responsibilities for secure collaboration
Managing risks and compliance requirements unique to cross-organization communication
Implementing technical and procedural safeguards to maintain confidentiality and integrity during data transfers
With these guidelines, ISO/IEC 27010 helps ensure that organizations can collaborate securely, building the trust necessary for joint ventures, partnerships, and international operations.
ISO/IEC 27011
Tailored specifically for the telecommunications sector, this standard provides industry-focused guidance to help telecommunications organizations strengthen their information security management. Building on the framework established by ISO/IEC 27002, ISO/IEC 27011 addresses sector-specific risks and requirements.
By offering detailed recommendations, it supports organizations in effectively safeguarding data integrity, confidentiality, and availability—core principles critical to the telecom industry. For organizations navigating complex regulatory landscapes and demanding service continuity, ISO/IEC 27011 ensures that implemented controls are both robust and relevant to telecommunications operations.
ISO 27013
If you're considering streamlining both your information security and IT service management systems, ISO 27013 offers practical guidance for bringing these two standards together. Whether your organization already has ISO/IEC 27001 (focused on information security) or ISO/IEC 20000-1 (centered on IT service management) in place—or if you're planning to implement both from scratch—ISO 27013 can help you integrate them efficiently.
Here’s how ISO 27013 supports the integration process:
Coordinated Implementation: If you already have one standard established, ISO 27013 provides step-by-step advice for adding the other. For example, if your IT service management is up to ISO 20000-1 standards, it outlines how to incorporate information security controls from ISO 27001, and vice versa.
Simultaneous Adoption: For organizations starting fresh, ISO 27013 illustrates how to implement both standards side by side, reducing overlap and avoiding duplicated effort.
Unified Management Systems: The guideline emphasizes areas where the requirements of the two standards align, allowing you to develop common policies, procedures, and controls. This means less paperwork, streamlined audits, and more cohesive management overall.
Understanding Overlaps and Differences: ISO 27013 details the similarities and distinctions between ISO 27001 and ISO 20000-1. This helps you avoid confusion, harmonize documentation, and maintain compliance for both standards with less hassle.
By following the recommendations in ISO 27013, you can simplify your efforts, optimize resource use, and create a robust, integrated management system that addresses both information security and service delivery.
ISO/IEC 27014
When it comes to overseeing information security at the organizational level, ISO/IEC 27014 steps in with valuable direction. This standard lays out the principles and processes that support effective governance of information security, ensuring it remains aligned with business objectives and stakeholder interests.
At its core, ISO/IEC 27014 emphasizes:
Establishing clear governance structures that define roles, responsibilities, and accountability for information security across the organization.
Setting and communicating objectives for information security in line with the organization’s overall strategy, so leadership and all relevant stakeholders are on the same page.
Evaluating risk and performance by regularly assessing the effectiveness of the ISMS processes and making informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Continual monitoring and measurement, which involves tracking progress against information security goals and swiftly addressing any deviations.
Transparent reporting and communication so that top management, governing bodies, and others involved in the ISMS have timely and accurate updates on the state of information security.
The focus of ISO/IEC 27014 is to ensure that information security isn’t treated as a siloed IT concern, but rather as a crucial element of organizational governance—integrated, measured, and actively supported at every level.
ISO/IEC TR 27016
Offers information on the economics of information security, providing insights into valuing information and information security within an organizational context and making economically sound decisions regarding information security.
This guideline is especially useful for executive management, as it supports strategic decision-making around the allocation of resources for security controls. By focusing on the economic aspects, ISO/IEC TR 27016 helps organizations understand the financial consequences of their security decisions, reduce potential negative impacts to business objectives, and minimize financial losses.
Key benefits include meeting legal obligations, managing customer expectations, enhancing brand reputation, and ensuring the accuracy of financial reporting. Ultimately, ISO/IEC TR 27016 enables organizations to balance security investments with overall economic sustainability.
ISO/IEC 27017
Offers guidelines on information security controls for cloud services, supporting the existing advice within ISO/IEC 27002. This standard is particularly beneficial for organizations that store or process information in the cloud. ISO/IEC 27017 provides both cloud service providers and cloud customers with additional recommendations for implementing and managing cloud-specific security controls. It helps clarify shared responsibilities in cloud environments and addresses unique risks associated with cloud computing, ensuring that both sides understand their roles in safeguarding information.
ISO/IEC 27018
Establishes commonly accepted control objectives, controls, and guidelines for implementing measures to protect Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in accordance with the privacy principles in the cloud environment.
ISO/IEC 27019
ISO/IEC 27019 is tailored specifically to the energy industry, offering detailed guidance on strengthening the security of process control systems that oversee everything from energy generation to distribution and transmission. The standard addresses information security requirements for systems and technology that manage, monitor, and automate critical infrastructure within utilities.
Key areas covered by ISO/IEC 27019 include:
Security practices for process control and monitoring technologies (think digital controllers and automation platforms)
Protection measures for Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) components
Safeguards for networked communications within grid systems, including telemetry and remote control devices
Information systems and supporting components integral to the energy sector’s operational environment
By following ISO/IEC 27019, energy organizations can reduce risks to their process control environment, helping ensure safe, resilient, and reliable operation of their essential services.
ISO/IEC 27021
ISO/IEC 27021 zeroes in on what it takes to be competent in managing information security management systems (ISMS). Rather than centering on organizations or technical requirements, this standard lays out the knowledge, skills, and behaviors expected from individuals responsible for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS.
Here’s what ISO/IEC 27021 covers:
Defines the essential knowledge and abilities: Whether you’re an aspiring ISMS professional, hiring manager, certification body, or training provider, ISO 27021 spells out the specific competencies required. This includes understanding the foundational principles of information security, familiarity with ISO/IEC 27001 and related standards, risk management expertise, and the ability to apply these concepts in real organizational scenarios.
Guides professional development: The standard assists in identifying gaps and setting goals for ongoing learning, making it useful for anyone building or sharpening their ISMS skills.
Supports hiring and certification: Organizations can use its guidelines to recruit the right talent, while certification bodies reference it during professional assessments.
In practice, ISO/IEC 27021 ensures that those managing ISMS processes aren’t just following a checklist, but actually possess the practical know-how to adapt security measures to their organization’s context, support continual improvement, and address evolving risks.
ISO/IEC 27032
A guideline for cybersecurity, aiming to bridge the gaps between cyber security, network security, information security, and critical information infrastructure protection (CIIP).
ISO/IEC 27033
It focuses on network security, providing guidelines and best practices for designing, implementing, operating, monitoring, and maintaining secure networks. Check out this article to learn more about network security and GRC.
ISO/IEC 27701
This standard extends ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002 for privacy management, including the processing of personal data, and can serve as a basis for compliance with data protection laws and regulations.
ISO/IEC TR 27008
Guides evaluating the implementation and operation of information security controls, including those outside the scope of ISO/IEC 27002, offering a broader perspective on ISMS control effectiveness.
ISO/IEC TR 27016
Offers information on the economics of information security, providing insights into valuing information and information security within an organizational context and making economically sound decisions regarding information security.
One thing to remember:
The ISO/IEC 27000 series is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is designed to be flexible and adaptable to different types of organizations, industries, sectors, and environments. It does not prescribe specific solutions or technologies for information security.
Rather, it provides a set of principles and best practices that you can use to design and implement an ISMS that suits your organization's unique characteristics and requirements.
Implementation Roadmap
To effectively strengthen their information security management systems (ISMS), organizations must start a strategic implementation roadmap rooted in compliance with the ISO 27000 series standards. Primarily, the first big milestone of this journey is achieving ISO 27001 certification.
ISO 27001 certification signifies an organization's commitment to systematically managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It provides a robust structure for identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security risks, thereby enhancing trust among stakeholders, customers, and partners.
Once ISO 27001 certification is attained, organizations are well-positioned to extend their compliance efforts by pursuing additional standards within the ISO 27000 series, namely ISO 27701, ISO 27017, and ISO 27018. Each of these standards serves as a valuable extension to ISO 27001, offering distinct benefits and addressing specific aspects of information security and privacy management.
In essence:
Extending ISO 27001 certification to encompass ISO 27701, ISO 27017, and ISO 27018 enables organizations to fortify their information security posture comprehensively. By embracing these standards as integral components of their ISMS, organizations can enhance resilience, foster trust, and demonstrate a steadfast commitment to safeguarding information assets and respecting privacy rights.

Growing Adoption of ISO 27001
Organizations worldwide are recognizing the value of ISO 27001 certification, and recent figures underscore this momentum. According to a 2021 ISO survey, over 10,000 information technology firms alone had secured ISO 27001 certification—a testament to the global surge in adoption across industries.
But what’s behind this trend? As market expectations and regulatory pressures rise, certification is no longer just a badge—it's a business differentiator. When your organization can demonstrate certified adherence to international standards, you're signaling reliability and security to customers, partners, and regulators alike. This not only builds confidence but also offers a clear market advantage when competitors lack similar credentials.
How ISO 27000 Series of Standards Make Security Management More Efficient?
Some of the benefits of using the ISO 27000 series for your security management are:
Improved security performance: The ISO 27000 standards help you identify and prioritize your security risks, and implement appropriate controls to mitigate them. You can also monitor and review your security performance regularly, and take corrective actions when needed. This way, you can continuously improve your security posture and resilience.
Enhanced compliance: The ISO 27000 standards help you comply with various legal, regulatory, contractual, and industry requirements that apply to your organization. You can also use the ISO 27000 standards as a benchmark to compare your security practices with those of your peers and competitors.
Increased trust and reputation: The ISO 27000 standards help you communicate your security commitment and capabilities to your stakeholders and customers. You can also obtain an independent certification for your ISMS, which can provide an external validation of your security excellence. This way, you can increase your trustworthiness and reputation in the market.
Reduced costs and complexity: The ISO 27000 standards help you streamline and simplify your security processes and procedures. You can also avoid duplication and inconsistency in your security activities, and optimize your use of resources and technology. This way, you can reduce your operational costs and complexity.
Optimize cost-effectiveness: Leveraging the structured framework of the ISO 27000 series enables you to implement and maintain comprehensive security processes across all operations, without unnecessary expenditure. By focusing on what matters most and eliminating redundant controls, organizations can achieve robust security outcomes while remaining mindful of their bottom line.
Strengthened third-party data and intellectual property management: Compliance with the ISO 27000 series empowers organizations to handle third-party financial data and intellectual property with greater care and consistency. The standards provide a globally recognized framework for vetting, monitoring, and managing information shared with partners, vendors, and clients. By following internationally accepted best practices, organizations demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive assets and respecting the trust placed in them. This not only reduces risks related to improper data handling or breaches but also helps establish the company as a reliable and secure business partner—much like how financial institutions trust SWIFT’s robust security framework when exchanging international payments.
These benefits help solidify mutually beneficial relationships with clients and stakeholders, giving your organization a clear edge in competitive markets where security and trust are essential currencies.
Why Security Should Be Regarded as an Essential Investment
Viewing security as a necessary investment—rather than a discretionary expense—is crucial in today’s digital environment. Cyber threats are growing in frequency and sophistication, and the consequences of overlooking security are not limited to financial losses. Reputational harm, erosion of customer trust, and disruption of operations can often have an impact that lasts far longer than any immediate costs incurred from a breach.
Industry-recognized standards, such as those within the ISO 27000 series, advocate a proactive approach to risk management. By committing resources to robust security measures upfront, organizations can:
Reduce long-term costs: Preventing incidents is typically far less expensive than remediation and recovery after an attack. Regulatory penalties, legal fees, and loss of business can easily eclipse the cost of preventive security.
Safeguard reputation and trust: Customers and partners are increasingly discerning, favoring organizations that clearly demonstrate strong information security practices.
Stay ahead of emerging threats: A security-forward mindset ensures that systems and controls evolve along with the threat landscape, rather than scrambling to catch up after an incident.
In short, treating security as an integral investment is not merely about compliance—it’s about protecting the very foundation of your organization’s operations, relationships, and long-term success.
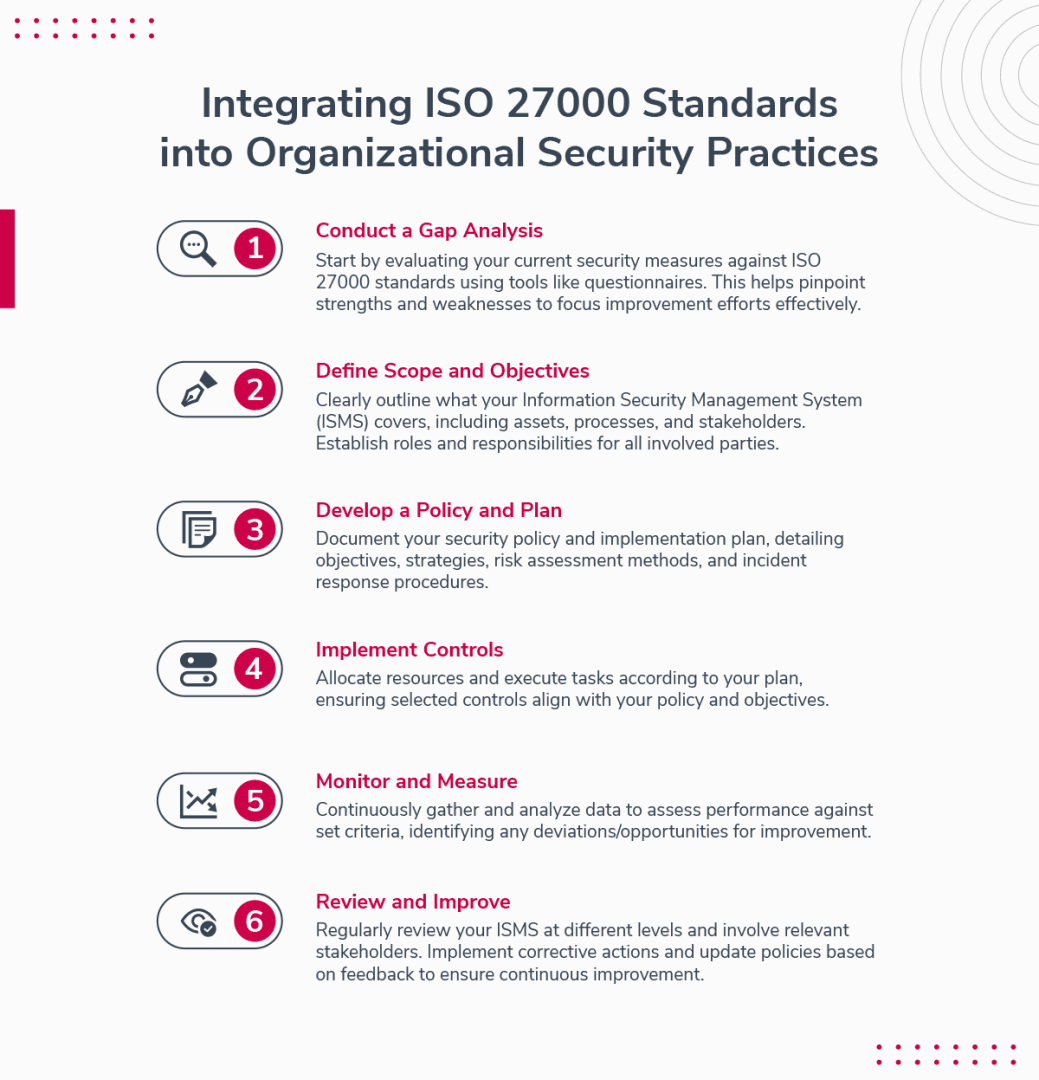
Strategies for Integrating ISO 27000 Standards into Organizational Security Practices
If you're interested in adopting the ISO 27000 series of standards for your security management, here are some strategies that can help you integrate them into your organizational security practices:
Conduct a gap analysis
The first step is to assess your current security situation and identify the gaps between your existing practices and the ISO 27000 requirements. You can use tools such as self-assessment questionnaires, checklists, or maturity models to perform this analysis.
This will help you understand your strengths and weaknesses, and prioritize your improvement actions.
Define the scope and objectives
The next step is to define the scope and objectives of your ISMS. You need to determine which information assets, processes, functions, locations, and stakeholders are included in your ISMS, and what are the expected outcomes and benefits of implementing it.
You also need to establish the roles and responsibilities of the people involved in your ISMS, such as top management, ISMS team, employees, suppliers, customers, etc.
Develop a policy and plan
The third step is to develop a policy and plan for your ISMS. You need to document your security policy that defines your security vision, mission, values, principles, goals, objectives, strategies, etc. You also need to document your plan that outlines how you will implement, operate, monitor, review, maintain, and improve your ISMS.
Your plan should include details such as risk assessment methodology, risk treatment options, control selection criteria, control objectives and measures, audit schedule, incident response procedure, training program, etc.
Implement the controls
The fourth step is to implement the controls that you have selected for your ISMS. You need to allocate the necessary resources, such as budget, time, staff, equipment, software, etc., and execute the tasks according to your plan.
You also need to ensure that the controls are effective, efficient, and consistent with your policy and objectives.
Monitor and measure
The fifth step is to monitor and measure your ISMS performance and compliance. You need to collect and analyze data and information from various sources, such as logs, reports, surveys, audits, tests, etc., and evaluate the results against your objectives and criteria.
You also need to identify and report any deviations, nonconformities, incidents, or opportunities for improvement.
Review and improve
The sixth and final step is to review and improve your ISMS. You need to conduct periodic reviews of your ISMS at different levels, such as operational, tactical, and strategic, and involve different stakeholders, such as top management, ISMS team, employees, suppliers, customers, etc.
You also need to implement corrective and preventive actions based on the findings and feedback from your reviews, and update your policy and plan accordingly.
What about the certification process?
How to Get ISO 27001 Certified
So, how do you get there? Let's break it down.
1) Understanding ISO 27001
Start with a deep understanding of ISO 27001 requirements and its controls. This foundational knowledge is critical for effectively planning and implementing your ISMS.
2) Planning and Role Assignment
Detailed planning involves defining the scope of your ISMS, identifying relevant stakeholders, and assigning roles and responsibilities within your organization to manage the certification process.
3) Scope Definition
Clearly define the scope of your ISMS, considering the information assets that need protection, the organizational areas involved, and the technologies used.
4) Policy, Procedure and Controls
Develop comprehensive policies, implement procedures and deploy technical, administrative, and physical controls that address the 93 requirements in ISO 27001 Annex A.
5) Risk Assessment and Gap Analysis
Conduct a formal risk assessment to identify security threats and vulnerabilities, followed by a gap analysis to determine the difference between your current state and the ISO 27001 requirements.
6) Statement of Applicability and Risk Treatment
Create a Statement of Applicability (SOA) that documents which controls you've implemented and why, along with a Risk Treatment Plan outlining how you plan to address identified risks.
7) Training and Awareness
Ensure all employees receive training on the importance of information security and their role in maintaining the ISMS.
8) Documentation and Evidence Collection
Prepare documentation and collect evidence of your ISMS's effectiveness, demonstrating that policies and controls are properly implemented and operational.
9) Internal Audit
Conduct an internal audit to assess the ISMS's conformity to ISO 27001 standards and identify areas for improvement.
10) External Audit and Certification
Undergo an external audit by a certification body. This process typically involves a two-stage audit: the first stage reviews your ISMS documentation, and the second stage assesses the effectiveness of your ISMS in practice.
11) Continuous Improvement
After certification, maintain and continually improve your ISMS through regular reviews, updates to security practices, and surveillance audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
Real-Life Examples and Scenarios of ISO 27000 Standards Application
To illustrate how the ISO 27000 standards can make your security management more efficient, here are some real-life examples and scenarios of how other organizations have applied them:
A global bank used ISO 27001 to enhance its security governance and risk management, and achieved a 30% reduction in security incidents, a 50% reduction in audit findings, and a 70% increase in customer satisfaction.
A healthcare provider used ISO 27001 to comply with the Security Controls required under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and improved its security awareness, culture, and practices among its staff and partners.
Competitive Advantage and Industry Trust
ISO 27001 doesn’t just strengthen your internal security posture—it can also give you a clear edge over competitors. Businesses across sectors increasingly look for partners that demonstrate a proven commitment to information security, especially when handling sensitive financial data or intellectual property. By meeting an internationally recognized standard, organizations show prospective clients and partners that they take data protection seriously.
A 2021 ISO survey reported that more than 10,000 information technology companies worldwide were ISO 27001 certified—highlighting the growing trend of organizations using certification as a way to build credibility and win more business. When your organization is compliant and your competitors are not, sales prospects are far more likely to choose you as a trusted partner.
These examples and trends show that applying ISO 27000 standards can deliver real, measurable benefits—both by improving internal operations and by establishing trust and confidence in the eyes of customers, regulators, and business partners.

Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
One of the key principles of ISO 27000 is that an ISMS should be continuously improved and adapted to changing circumstances.
This means that you should not treat your ISMS as a static or one-time project, but rather as a dynamic and ongoing process that evolves with your business needs, risks, and opportunities.
By doing so, you can ensure that your ISMS remains relevant, effective, and aligned with your strategic objectives.
At its core, ISO 27000 emphasizes a proactive approach to managing information security and information risks through the appropriate implementation of controls within your Information Security Management System (ISMS). This approach is not just about putting controls in place and checking the box; it’s about regularly assessing those controls, understanding emerging threats, and adapting your security measures to ensure long-term protection of your information assets.
By embracing this philosophy, organizations can move beyond mere compliance and foster a culture of continuous improvement, where information security becomes an integral part of day-to-day operations and decision-making.
But how can you achieve continuous improvement and adaptation in your ISMS?
Here are some steps that you can follow:
1) Establish a regular review cycle for your ISMS
This involves monitoring and measuring the performance of your ISMS against the objectives, policies, and controls that you have defined. You should also conduct internal audits and management reviews to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of your ISMS.
2) Identify and analyze the gaps, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement in your ISMS
This involves collecting feedback from various sources, such as stakeholders, customers, employees, regulators, and external auditors. You should also consider the changes in the internal and external environment that may affect your ISMS, such as new technologies, threats, regulations, or business processes.
3) Implement corrective and preventive actions to address the issues and enhance the strengths of your ISMS
This involves prioritizing and planning the actions based on their impact, urgency, and feasibility. You should also document the actions and assign responsibilities and resources for their execution.
4) Verify and validate the results of the actions
This involves checking whether the actions have achieved the desired outcomes and resolved the problems. You should also monitor and measure the effects of the actions on your ISMS performance and report them to the relevant stakeholders.
5) Learn from the experience and update your ISMS accordingly
This involves incorporating the lessons learned from the actions into your ISMS documentation, such as policies, procedures, objectives, controls, risk assessments, etc. You should also communicate the changes to your ISMS to all the parties involved and provide them with appropriate training and awareness.
By following these steps, you can create a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation in your ISMS that will help you achieve higher levels of information security maturity and excellence.
Examples and Scenarios - Continuous Improvement
To illustrate how continuous improvement and adaptation work in practice, let's look at some examples and scenarios from different industries and sectors.
1) A healthcare organization implemented an ISMS based on ISO 27001 to protect its sensitive patient data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or modification. However, after a few months of operation, it discovered that some of its employees were using weak passwords or sharing them with others.
To address this issue, it conducted a password audit to identify the users who were violating the password policy. It then implemented corrective actions such as:
Resetting the passwords
Enforcing password complexity rules
Educating the users about password security best practices
Monitoring password usage patterns.
It also updated its password policy to reflect the current standards and requirements.
2) A financial institution implemented an ISMS based on ISO 27001 to comply with the regulatory requirements for information security in its industry. However, after a year of operation, it faced a cyberattack that exploited a vulnerability in one of its software applications.
To address this issue, it conducted a root cause analysis to determine how the attack happened and what damage it caused. The financial institution then implemented preventive actions such as:
Patching the vulnerability
Enhancing its firewall settings
Conducting penetration testing
Updating its incident response plan
Notifying its customers about the breach.
It also updated its risk assessment to include new threats and vulnerabilities that it identified from the attack.
Key Takeaways
Understand ISO/IEC 27000 Series: It's a suite of standards aimed at guiding organizations in establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
ISO/IEC 27001 is Central: This standard sets out the requirements for an ISMS, focusing on a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information securely.
Compliance and Improvement Cycle: Embrace the Plan-Do-Check-Act methodology to continually refine your ISMS, ensuring it remains effective against emerging threats.
Targeted Standards for Enhanced Security: Utilize specific standards like ISO/IEC 27017 for cloud security and ISO/IEC 27018 for personal data protection to address particular aspects of your security needs.
Certification Process: Achieving ISO 27001 certification involves understanding the standard, defining the ISMS scope, developing policies, conducting risk assessments, and undergoing audits, underscored by a commitment to continuous improvement. It’s important to note that while the ISO 27000 family of standards provides the framework and vocabulary for information security, there is no such thing as an “ISO 27000 certification.” Certification is only available for ISO 27001, which is the core certifiable standard in the series. You can certainly align your practices with other standards in the 27000 series, but formal certification is issued exclusively for ISO 27001.
Real-world Application: ISO/IEC 27000 series standards are proven to bolster security governance, risk management, and compliance, contributing to significant reductions in security incidents and enhanced stakeholder confidence.
Commitment to Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update your ISMS to keep pace with technological advancements and the evolving security landscape.
Holistic Security Management: Streamline your approach by managing security holistically—responsible governance isn’t just about technology, but also about investing in ongoing education and training. Empower your teams with up-to-date best practices to foster a culture of security awareness and accountability across your organization.
By implementing these key takeaways, organizations can not only meet compliance requirements but also build a resilient framework that adapts to change, addresses new risks proactively, and cultivates a strong security posture at every level.







