Published on: Jan 18, 2024
ISO 42001 Essentials: Building Trust And Mastering Compliance in the AI Era
Get up to speed with ISO 42001, the latest standard set to shift how you manage AI risks and ethical considerations.
In this article, we'll cover the must-know aspects and how they impact your organization's AI practices. Moreover, for those of you already familiar with ISO 27001, we'll illustrate how you can integrate its principles with ISO 42001 to streamline your compliance processes.
Let's begin!
AI and Compliance: Current State and the Need for ISO 42001
In 2023, AI's landscape dramatically shifted. Its global adoption drove economic growth and enhanced customer experiences. Yet, it also highlighted the need for ethical AI practices.
As AI integrates into various sectors, a standard framework for managing risks and ethics is crucial. Here is where ISO 42001 importance grows. It aligns with the growing call for ethical AI globally.
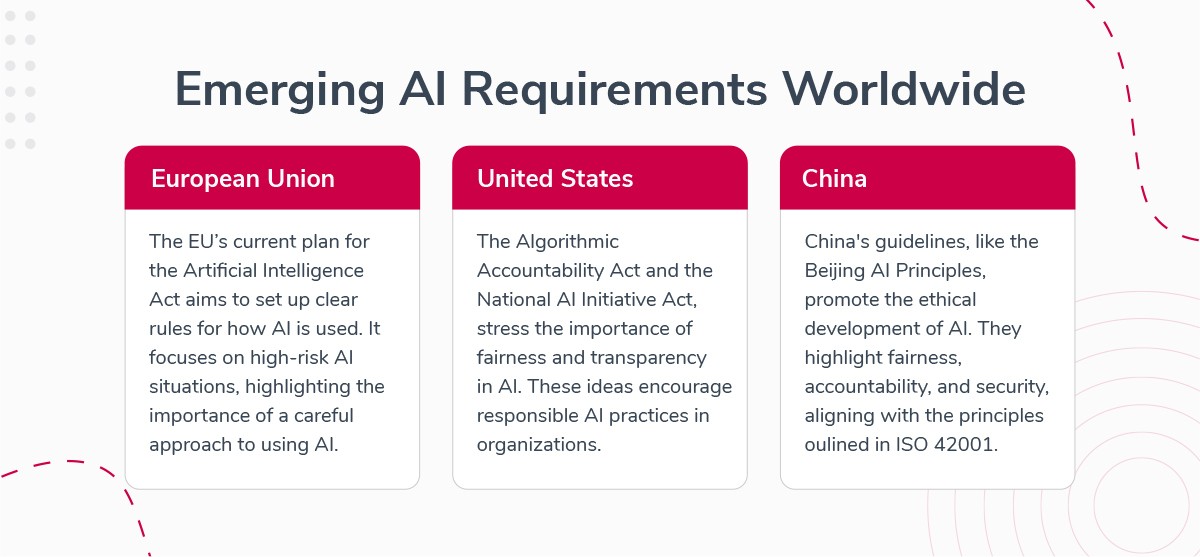
There are notable developments regarding AI requirements worldwide. Let's talk about some of them.
The European Union's proposal for the Artificial Intelligence Act aims to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for AI applications. This Act, focusing on high-risk AI applications, underscores the importance of a systematic approach to AI deployment. An approach that this new ISO standard directly addresses.
Similarly, initiatives in the United States, such as the Algorithmic Accountability Act and the National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act, emphasize fairness and auditability in AI. These principles align closely with the core principles of ISO 42001, promoting responsible AI practices within organizations.
advocate for ethical AI development. These guidelines emphasize fairness, accountability, and security. They underscore ISO 42001's relevance in today's tech landscape.
In summary, the evolving landscape of AI regulation reflects a pressing need for standards that ensure ethical and responsible AI practices. ISO 42001 emerges as a pivotal response to this global call, offering a structured approach to managing the complexities and risks associated with AI technologies.
Its introduction is timely and essential in guiding organizations towards responsible AI deployment that aligns with the international regulatory momentum.
ISO 42001 AI Compliance: Applicability and Benefits
The introduction of ISO 42001 in December 2023 marks a major advancement in AI governance. As an international management system standard, it emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach to managing the risks inherent in the development and deployment of AI technologies.
This standard is critical in promoting a culture of responsibility, safety, fairness, and security in AI applications.
ISO 42001 is designed to be universally applicable, making it relevant for a wide range of organizations. Whether a company is directly developing AI technologies or utilizing AI-powered products and services, this new standard provides a framework adaptable to various contexts and scales.
Let's check the benefits of adopting the new framework:
1 - Strategic Integration into Organizational Governance
ISO/IEC 42001:2023 prompts organizations to consider AI implementation as a strategic decision. It fosters the adoption of robust governance practices, aligning AI initiatives with overarching business goals and risk management strategies. This standard facilitates informed decision-making processes at the organizational level.
2 - Harmonizing Governance and Innovation
Recognizing the importance of striking a balance between governance and innovation, ISO/IEC 42001:2023 empowers organizations to leverage the benefits of AI while maintaining responsible and accountable practices. It encourages a dynamic balance between harnessing innovation and safeguarding ethical considerations in the development and deployment of AI systems.
This approach offers a holistic perspective, mitigating potential risks and fostering positive outcomes in artificial intelligence.
3 - Implementation of Robust Safeguards
ISO 42001 mandates the establishment of all-encompassing safeguards, equipping organizations with the necessary tools to address risks associated with AI. By incorporating these safeguards, organizations can proactively minimize potential harm and safeguard the interests of stakeholders, thereby enhancing overall AI system resilience.
4 - Demonstration of Commitment to Ethical AI Practices
ISO/IEC 42001:2023 certification serves as tangible proof of an organization's unwavering commitment to the ethical development and application of AI. It showcases the establishment of robust governance structures, effective risk management, and adherence to compliance protocols, supporting responsible AI practices.
5 - Effective Management of Continuous Learning in AI Systems
Given the inherent continuous learning capabilities of AI systems, ISO/IEC 42001:2023 provides a framework for organizations to establish safeguards and processes.
Now, let's review the requirements.
ISO 42001 AI Compliance: Requirements
The structure of ISO 42001 is somewhat similar to ISO 27001. There are Mandatory Clauses in the main standard document (Clauses 4 to 1) and Annex A provides a list of required controls that must be deployed based on scope and the Statement of Applicability.
Mandatory Clauses
Implementing ISO 42001 involves a series of mandatory clauses that guide organizations in establishing a robust Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS). These include:
Organizational Context and Stakeholder Analysis:
Determine the context of the organization.
Identify interested parties and stakeholders.
Understand their needs and expectations.
Document the scope of AIMS.
Training and Awareness Programs:
The implementation of comprehensive training and awareness programs is paramount for companies involved in the development and utilization of AI systems. These programs help:
Implement comprehensive training to deepen understanding of ethical, social, and technical aspects of AI.
Ensure employees are aware of ethical considerations, biases, and risks in AI algorithms. This will enable them to make informed decisions throughout the development lifecycle.
AI Policy and Leadership Commitment:
Objectives related to the use of AI systems must be properly documented, tracked, and reported to leadership.
Develop and document an AI policy.
Demonstrate leadership commitment through resource allocation, planning, and management reviews.
Establish a continual improvement program.
AI Risk Assessment Process (Section 6.1.2):
To comply with the AI risk assessment requirements outlined in section 6.1.2, organizations must do the following:
Establish a consistent, valid, and comparable AI risk assessment process. This process, aligned with the organization's AI policy and objectives, should ensure consistency, validity, and comparability in repeated assessments.
Identify and analyze risks affecting AI objectives.
Evaluate risks against predefined criteria and prioritize treatment.
Risk Treatment and Controls:
Select appropriate treatment options based on risk assessment results.
Ensure necessary controls are in place, in line with those specified in Annex A.
Assess the need for additional controls beyond Annex A for comprehensive risk management.
Internal Audit Requirement:
Finally, just as it is required by ISO 27001, an internal audit process must be in place to evaluate the effectiveness of the program on an annual basis.
Let's move on to Annex A.
Annex A
Annex A outlines the key requirements across various aspects of AI system development and usage. Let's talk about them:
In the domain of policies (A.2), organizations are mandated to formulate and document an AI policy. This ensures it aligns with other organizational policies and undergoes periodic reviews to maintain effectiveness.
The internal organization (A.3) needs the definition of roles and responsibilities for AI, fostering accountability, while also establishing a process for reporting concerns throughout an AI system's lifecycle.
Addressing resources (A.4), organizations must comprehensively document various aspects, including data, tooling, systems, computing, and human resources. All these ensure a holistic understanding and management of resources to address risks.
In the assessment of impacts (A.5), organizations are required to establish processes for AI system impact assessments, documenting and retaining the results to assess potential consequences on individuals or societies throughout the AI system's lifecycle.
In the AI system life cycle (A.6), emphasis is placed on setting objectives for responsible development, defining processes for design and development, and specifying requirements, design, and validation measures.
Data for AI systems (A.7) involves processes related to data management, acquisition, quality, provenance, and preparation.
Information for interested parties (A.8) underscores the importance of providing relevant information to users, reporting incidents, and ensuring communication about the AI system.
To ensure responsible use (A.9), organizations are required to define processes and objectives, ensuring the intended use aligns with documentation.
Finally, in third-party and customer relationships (A.10), organizations must allocate responsibilities, establish processes for supplier relationships, and consider customer expectations in the responsible development and use of AI systems.

ISO 42001 and ISO 27001: An Integrated approach
You can smoothly integrate ISO 42001. They benefit from the similar structures and goals of both standards. This approach streamlines processes and boosts efficiency.
The information security management system (ISMS) of ISO 27001, with its focus on safeguarding information assets, pairs well with ISO 42001, which focuses on responsible AI system development and usage.
Their shared structure extends to policies, risk assessments, and controls. This similarity prevents effort duplication. Aligning their objectives promotes effort consolidation, especially in risk management and controls. As a result, organizations achieve a more unified and effective management strategy.
A few areas and processes can be integrated:
Risk Assessment
Nonconformity and Continual Improvement
Incident Management
Management Review
Among other similar areas/requirements.
By adopting an integrated approach, companies can derive synergies in monitoring and evaluating the performance of their information security and AI management systems. You can consolidate regular audits and assessments, reducing redundancy and promoting a more efficient use of resources.
Additionally, you can implement a unified approach to training and awareness programs, addressing the shared need for educating personnel on information security and responsible AI practices.
Key Takeaways
As AI technology continues to grow, ISO 42001 emerges as a crucial standard for managing AI risks and ensuring ethical practices. It aligns with global regulatory trends and offers a structured approach to responsible AI deployment.
ISO 42001 is universally applicable across various industries, fostering a culture of safety, fairness, and security in AI applications. Its adoption can lead to enhanced risk management, improved stakeholder trust, streamlined compliance, and a competitive advantage.
Implementing ISO 42001 involves addressing challenges like resource constraints, cultural barriers, and technical complexities. Solutions include a phased approach, effective communication, and leveraging technology solutions like StandardFusion.
Key requirements include establishing an AIMS, documenting AI policies, conducting comprehensive training, and performing regular risk assessments and audits. Annex A provides detailed guidance on policies, internal organization, resources, impact assessments, and more.
For those already certified in ISO 27001, integrating ISO 42001 can streamline processes and enhance overall efficiency. Similarities in structure and objectives between the two standards facilitate a cohesive management approach.
Are you ready to embrace ISO 42001 and lead the way in ethical AI practices?
Let's elevate your approach to ISO 42001 with StandardFusion, where compliance becomes a strategic advantage. Connect with our team and learn more about how you can experience the ease of mapping controls to frameworks, tracking compliance in real-time, and automating tasks.







