Mar 29, 2017
Why Use Standard Agnostic Controls in your Compliance Program
The adoption of a corporate-wide compliance program is one of the most demanding projects you may undertake. Furthermore making the most of time-consuming tasks such as controls implementation, requires not only the experience and knowledge but also a holistic approach at the design level.
Every organization is different. Standards were created keeping in mind that they would be implemented by companies and industries around the globe, from diverse sectors and sizes. Various standards that cover similar content or correlated disciplines may present you with a great opportunity for effort optimization, so that once implemented controls may be used for meeting one or more requirements, even from completely different standards.
Getting the terminology right is an important step towards control optimization. Make sure everyone is on the same page and understands the differences between these two terms:
Requirement: A statement that identifies a necessary point of action, dictated by a standard your organization complies to and, most of the times, mandatory.
Control: A standard-agnostic means of meeting one or more requirements, from the same or even multiple standards.
This simple approach allows you to re-use controls across multiple standards. Take for example ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS. Once you have developed and implemented the information security policy required by ISO 270001 "A.5 Information security policies", the same control can be used to meet the PCI-DSS requirement 12: "Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel." To do so, you must ensure that your controls are designed with agnostic properties in mind.
The key here is to understand the basic difference of compliance requirements to control implementation. If your company must implement a mandatory control for compliance, that is where your focus should be, while ensuring that the team responsible for the actual implementation takes every step to use an agnostic approach aligned to the corporate strategy.
Below you can see at a high-level the mapping of the 12 PCI DSS requirements to ISO/IEC 27001:2013 clauses, courtesy of ISACA:

As you can see, there is quite a bit of overlap from a payment card developed standard and the most well-known and worldwide implemented information security standard, ISO 27001.
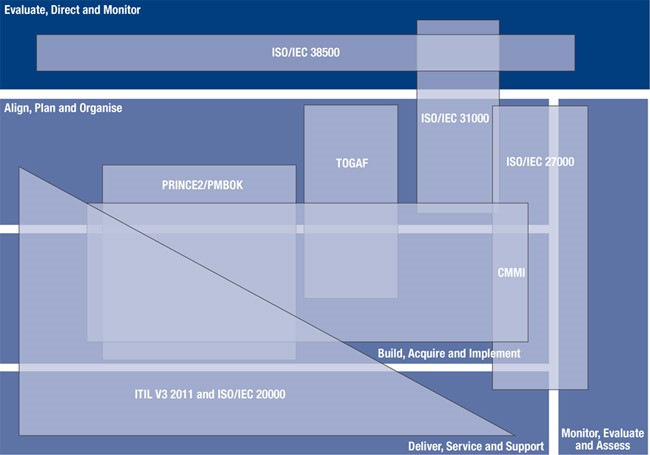
The diagram above is from COBIT 5 and creatively shows how different standards, norms, best practices interconnect and complement each other. While not displayed, one could also argue that ISO 20000 and ITIL V3 2011 also have information security and business continuity aspects, so there could be an intersection with ISO 27001 and ISO 22301.
It quickly becomes evident how much overlap there is between various standards, the use of standard-agnostic controls simplifies the process of implementation and management of your compliance programs.







